Ever thought about why bicycles are so good at turning your pedaling into movement? It’s all about physics and mechanics. These principles turn your energy into motion. This shows how does a bicycle work and the science behind moving forward.
Bicycles use momentum, force, and friction to move. This lets riders go places easily. Let’s dive into how this magic happens.

Understanding Bicycles: A Brief Overview
Bicycles are a blend of engineering and human ability. The history of bicycles started in the 1790s. Early models like the Celerifere didn’t have pedals or steering. But, innovators like Baron Karl von Drais added steering, making bikes better.
By the late 1800s, bikes got even more advanced. The chain drive system improved their performance and use. Today, bikes come in many designs and materials.
Modern bikes often use aluminum alloy or carbon fiber for their frames. These materials make bikes strong and light. Other materials like steel, titanium, and magnesium are used in special bikes.
There are also different types of bikes, like full-suspension and hardtail mountain bikes. Full-suspension bikes have a linkage system for smooth movement. Hardtail bikes have basic suspension forks.
The world of bike wheels has also changed a lot. Mullet wheelsets use different sizes for better agility and clearance. Bike rims are usually made of aluminum or carbon fiber, with steel spokes. New ideas keep coming, like electric bikes for all kinds of riders.
How Does a Bicycle Work: The Science Behind It
The mechanics of a bicycle are quite interesting. They show how energy changes and affects bike movement. When you pedal, your effort turns into kinetic energy, making the bike move.
This change is key for moving forward. It shows how well bicycles work as a way to get around.
The Role of Energy Conversion in Bike Operation
Every time you cycle, energy changes happen. For road cyclists, about 80% of resistance comes from air. This affects how well you can cycle.
By improving how energy changes, riders can go faster. They use aerodynamics to cut down on energy loss. This makes them go further without getting tired.
What is Kinetic Energy in Cycling?
The kinetic energy in cycling depends on the bike’s speed and how much it weighs. Newton’s Laws explain how pedaling makes the bike go faster or slower.
At speeds over 5 mph, the bike stays stable because of its momentum. Knowing this helps cyclists ride better and faster.
Bicycle Anatomy: Components that Make It Function
Knowing how a bicycle works is key to keeping it in top shape. Each part is important for a smooth ride. From the frame to the mechanical bits, they all work together.

The Importance of the Frame and Structure
The frame is the heart of the bike, giving it strength and support. Old bikes were made of steel, but now most use aluminum alloy, which is lighter and more durable. High-end bikes might feature materials like carbon fiber or titanium for superior performance.
Choosing the right frame size is also crucial for comfort and efficiency, and that’s where a bike size chart comes in handy. The most common design is the diamond frame, made of six tubes in two triangles. The choice of material and the proper frame size both affect the bike’s weight, strength, and overall riding experience.
Parts of a Bike: Speaking the Language of Mechanics
Knowing the bike’s parts is important. It helps you understand how it works. Here are some key parts:
- Wheels: They come in different sizes and styles for various biking needs.
- Brakes: Rim brakes are common because they’re cheap and easy to fix. But disc brakes are better in rainy weather.
- Drivetrain: This includes the cassette, derailleur, and chain. They help you change gears smoothly.
- Pedals: Clip-in pedals keep your feet in place better than flat pedals.
- Fork and Handlebars: They help you steer and control the bike.

Learning about bike parts helps you take care of your bike better. Knowing what each part does lets you fix problems quickly. It keeps your bike running well and makes riding more fun.
How Bicycle Wheels Work: The Foundation of Mobility
Bicycle wheels are key to how bikes move and perform. Knowing how they work helps us see their importance in the cycling experience. Every detail, from size to design, affects speed and balance. This makes choosing the right bike a big deal for riders.
How many wheels does a bicycle have?
A standard bicycle typically has two wheels, optimized for balance, speed, and maneuverability. This configuration has evolved to provide an efficient riding experience for daily commutes and recreational use.
Variations include:
- Tricycles (3 wheels): Offer extra stability, commonly used by children, adults with balance issues, or for cargo transport.
- Quadricycles (4 wheels): Provide greater stability and are often used for recreational rides or by multiple riders.
- Pentacycles (5 wheels): Rare designs, usually experimental or historical, featuring a larger central wheel supported by smaller ones.
Bicycle wheels are crucial for stability and smooth motion, supporting the rider’s weight.
While a bicycle’s two-wheel design seems simple, the mechanics behind it are complex. Whether for daily commutes or recreational rides, understanding how bicycle wheels work helps riders appreciate this engineering achievement.
The Impact of Wheel Size on Speed and Balance
Wheel size is crucial for speed and balance. Bigger wheels give smoother rides and more momentum, helping cyclists go faster. They also make the bike more stable, especially on rough paths or sharp turns.
Choosing the right wheel size can make your bike easier to handle. It can also make your rides more fun.
How Spoked Wheels Enhance Performance
Spoked wheels play a crucial role in enhancing a bike’s performance by distributing weight evenly and reducing drag. This makes the bike more efficient and easier to maneuver. With properly tensioned spokes, bikes can accelerate and turn more smoothly, improving performance in various cycling conditions.
To maintain this efficiency, it’s important to regularly tighten bicycle spokes, as loose spokes can affect the wheel’s stability and performance. Properly tensioned spokes ensure a smoother ride and prevent potential damage to the wheel.

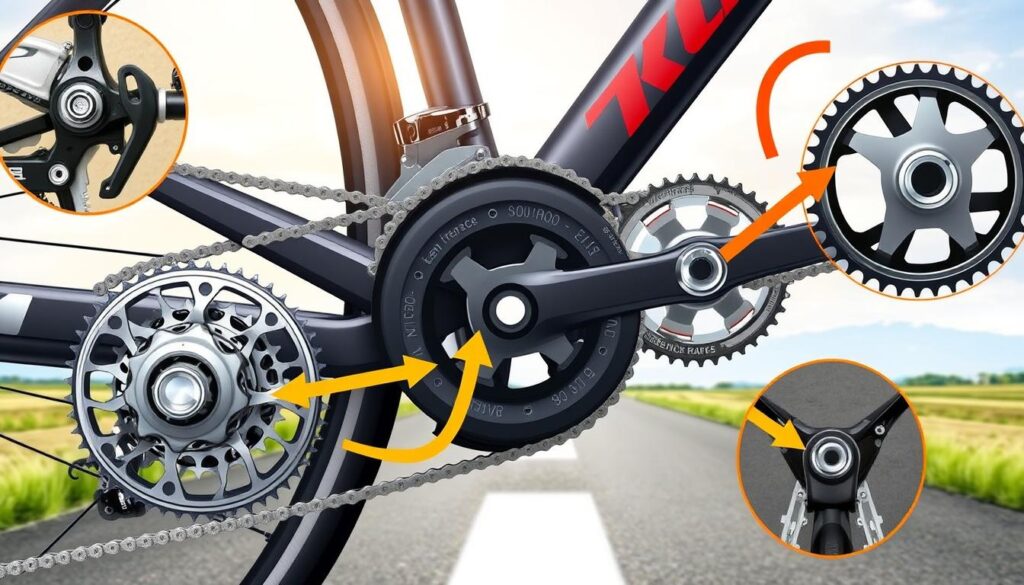
Understanding Bicycle Gears: Enhancing Efficiency
Bicycle gears are key to better cycling. They help riders adjust to different terrains and speeds. Knowing how bicycle gears work can greatly improve your ride. Mastering how to shift gears makes cycling easier and helps save energy, improving both your ride and overall performance.
How Gears Influence Pedal Functionality
Gears and pedals work together for a smooth ride. Gears affect how much effort you need to keep moving, especially uphill or when speeding up. A bigger chainring means you cover more ground with each pedal, perfect for flat areas and fast rides.
On the other hand, smaller gears are better for hills. They make pedaling easier but require more turns to move forward.
The Significance of Gear Ratios
Gear ratios are crucial for a bike’s performance. They’re found by dividing the chainring teeth by the rear cog teeth. For example, a 40-tooth chainring with an 18-tooth cog gives a 2.22:1 ratio.
This ratio shows how far you’ll go with each pedal. It affects your efficiency. Gear ranges vary in difficulty, with higher ratios being tougher. Riders need to pick the right gear ratios for their skill and the terrain.

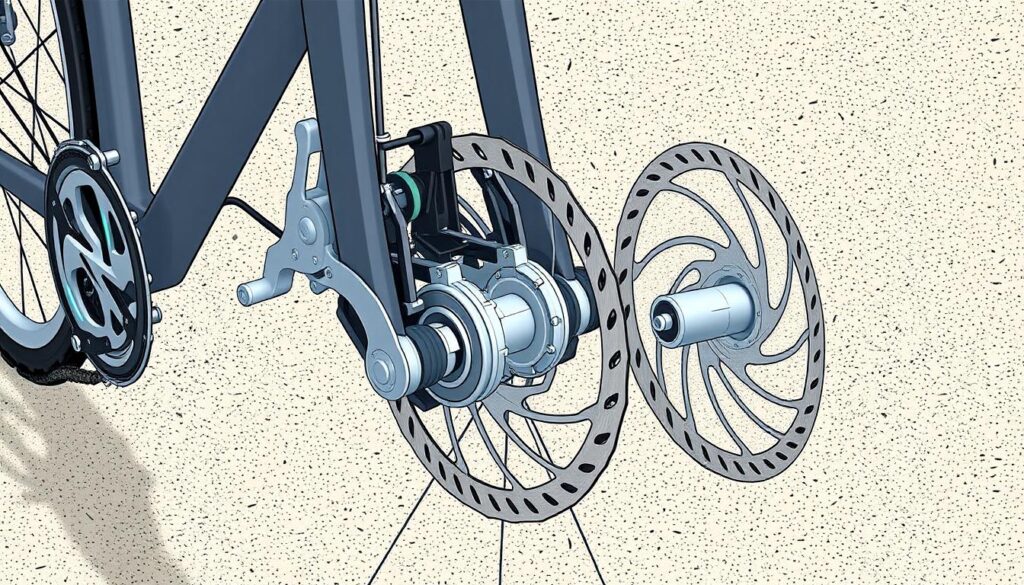
How Bicycle Brakes Work: Safety Mechanisms Explained
Bicycle brakes are key to keeping riders safe by stopping the bike quickly. They work by using friction to slow down the bike. When you press the brake lever, the pads rub against the wheels or rotors.
This rubbing creates friction, which turns the bike’s energy into heat. This heat helps slow the bike down until it stops.
Friction and Its Role in Stopping the Bike
Friction is the main force behind bicycle brakes. When you apply the brakes, the pads press against the rims or rotors. This creates resistance that slows or stops the bike.
Keeping the brake pads in good shape is crucial for safety. Weather and the surface you’re riding on can affect how well the brakes work. So, it’s important to check and maintain them regularly.
Different Types of Bicycle Brakes: Pros and Cons
There are many types of bicycle brakes, each with its benefits and drawbacks:
- Rim Brakes: They’re cheap and easy to fix. But, they don’t work well in the rain and need new pads often.
- Disc Brakes: They’re getting more popular because they work well in all weather. They stop the bike stronger and don’t care about the wheel’s condition.
- Cantilever Brakes: These are great for mountain bikes. They work well off-road but need more adjustments.
- Coaster Brakes: They’re simple and reliable, often found on kids’ bikes. They only stop the back wheel and can cause skidding if not used right.
Choosing the right brake depends on your riding style and where you ride. Knowing how different brakes work can make your rides better.
How Bicycle Handlebars Work: Steering and Control
Handlebars are key for steering and controlling a bike. Their design affects how easy it is to steer and how comfortable you feel. Knowing about different handlebars helps riders control their bikes better on various terrains.
The Function of Handlebars in Steering Mechanics
Good steering is crucial for a safe and fun ride. Handlebars let riders steer by using their body weight and strength. There are several types of handlebars:
- Drop Handlebars: These are common on road and track bikes, with different styles like standard and ergo.
- Flat Bars: Found on mountain and hybrid bikes, they are nearly straight and stable.
- Bullhorn Handlebars: Used on triathlon bikes, they curve up for track and fixed-gear bikes.
- Riser Bars: A flat bar variation that rises, making climbs more comfortable.
Leverage and Stability: The Physics of Steering
Steering physics is all about leverage and stability. Wider handlebars help control the bike, especially at high speeds. Brands like Salsa Cycles and SOMA Fabrications make handlebars for off-road riding.
Riders can pick handlebars based on their biking style. Whether for triathlons or city rides, there’s a handlebar for everyone.

Understanding how a bicycle works shows the deep connection between physics and mechanics. It has evolved from simple wooden designs to modern bikes with advanced tech. The gears, brakes, and frames work together to make our energy-efficient movement.
The average bike can go 16 to 25 kilometers per hour. This is five to six times faster than walking. The pneumatic tire and gearing systems have made cycling better and more accessible to many.
Now, with electric bikes and new materials, cycling keeps getting better. It’s a key way for over 1 billion people to get around.
Learning about bicycle mechanics makes us appreciate this amazing invention more. It also shows how important it is to take care of our bikes and ride safely. By cycling, we help make the world a healthier and greener place.






